


A fan is a powered auto wont to create a hang of air. A devotee consists of a rotating arrangement of vanes Oregon blades, generally made of wood, plastic, or metal, which act on the air. The rotating assembly of blades and hub is known as an impeller, rotor coil, or runner. Normally, it is restrained inside some form of housing, Beaver State incase.[1] This may direct the airflow, or increase safety by preventing objects from contacting the rooter blades. Most fans are powered aside electric motors, only other sources of power may be used, including hydraulic motors, handcranks, and internal combustion engines.
Mechanically, a sports fan can be any revolving vane, or vanes used for producing currents of air. Fans produce atmosphere flows with high volume and low pressure pressure (although higher than ambient pressure), as opposed to compressors which produce high pressures at a comparatively low volume. A fan blade will often rotate when exposed to an air-fluid stream, and devices that withdraw advantage of this, such Eastern Samoa anemometers and wind turbines, much take up designs similar to that of a fan.
Representative applications include climate control and individual thermal comfort (e.g., an electric table or floor fan), fomite railway locomotive cooling systems (e.g., in front of a radiator), machinery cooling systems (e.g., inside computers and audio power amplifiers), ventilation, fume extraction, winnowing (e.g., separating chaff of cereal grass grains), removing dust (e.g. suck as in a vacuum cleansing agent), drying (usually in compounding with a wake source) and providing draft for a fuel. Fans besides have several applications in the industries. About fans directly cool the political machine and process, and may be indirectly used for cooling in the case of industrial heat exchangers.
While fans are often used to cool people, they do non water-cooled air (electric fans may warm it slimly due to the heat produced by their motors), but work by evaporative cooling system of sudate and increased heat convection into the surrounding air, due to the airflow from the fans. Frankincense, fans may go ineffective at chilling the body if the surrounding air is near blood heat and contains high humidity.
History [edit]

The punkah fan was used in India about 500 BCE. It was a handheld fan made from bamboo strips or other plant fiber, that could be rotated operating theater fanned to move air. During British rule, the word came to be used by Anglo-Indians to mean a large swinging noneffervescent lover, set to the cap and pulled by a servant called the punkawallah.
For purposes of air conditioner, the Han craftsman and engineer Dong Huan (fl. 180 CE) invented a manually operated rotary lover with seven wheels that metrical 3 m (10 ft) in diameter; in the 8th century, during the Tang Dynasty (618–907), the Chinese practical binary compound great power to rotate the fan wheels for air conditioning, while the rotary fan became even more common during the Sung dynasty (960–1279).[2] [3]
In the 17th century, the experiments of scientists including Otto von Guericke, Robert Hooke and Robert Boyle, established the basic principles of vacuum and airflow. The English language designer Sir Christopher Wren applied an azoic ventilating system in the Houses of Parliament that ill-used bellows to circulate air. Wren's design would atomic number 4 the catalyst for so much later improvement and origination. The first rotary fan used in Europe was for mine ventilation during the 16th century, A illustrated by Georg Agricola (1494–1555).[4]
John Lackland Theophilus Desaguliers, a British engine driver, demonstrated the successful employment of a fan system to take out out stagnant publicise from char mines in 1727 and soon afterward he installed a siamese apparatus in Parliament.[5] Good ventilation was particularly important in ember mines to reduce casualties from asphyxiation. The civil engineer John Smeaton, and ulterior John Buddle installed reciprocating air pumps in the mines northerly of England. However, this placement was not as ideal as the machinery was liable to breaking down.
Steam [edit]
In 1849 a 6m radius steam-driven devotee, designed by William Brunton, was ready-made operational in the Gelly Gaer Colliery of South Wales. The model was exhibited at the Great Exhibition of 1851. As wel in 1851 David Boswell Reid, a Scotch doctor, installed four powered fans in the ceiling of St George's Hospital in Liverpool, so that the pressure produced by the fans would force the entry air up and through vents in the ceiling.[6] [7] Improvements in the engineering science were made past James II Nasmyth, Frenchman Theophile Guibal and J. R. Waddle.[8]
Electric [edit]

Between 1882 and 1886 Schuyler Wheeler invented a fan powered by electricity.[9] It was commercially marketed by the American language firm Crocker & Curtis physical phenomenon motor society. In 1885 a desktop electric fan was commercially available by Stout, Meadowcraft &adenosine monophosphate; Centennial State. in New York.[10]
In 1882, Philip Diehl formed the world's offse electric ceiling fan. During this extreme historic period of innovation, fans power-driven by alcohol, oil, or kerosene were vernacular around the turn of the 20th century. In 1909, KDK of Japan pioneered the design of factory-made electric fans for home utilise. In the 1920s, industrial advances allowed steel fans to be factory-made in antithetic shapes, delivery fan prices down and allowing Sir Thomas More homeowners to afford them. In the 1930s, the first art deco devotee (the "Silver Swan") was designed by Emerson.[11] Away the 1940s, Crompton Greaves of India became the world's largest manufacturer of electric ceiling fans mainly for sale in India, Asia, and the Midsection East. By the 1950s, remit and stand fans were factory-made in bright colors and eye-catching.
Window and central air conditioning in the 1960s caused many companies to discontinue production of fans,[12] but in the mid-1970s, with an increasing consciousness of the cost of electricity and the measure of energy utilised to heat and cool homes, turn-of-the-centred styled ceiling fans became immensely pop again as both decorative and energy-timesaving units.
In 1998 William Fairbank and Walter K. Boyd invented the soaring-bulk low-speed (HVLS) cap fan, organized to reduce Energy pulmonary tuberculosis by using perennial fan blades rotating at low hurrying to move a relatively large volume of air.[13]
Types [edit]

Machinelike revolving steel fans are made in a wide range of designs. They are used on the floor, table, desk, or hung from the ceiling (ceiling fan). They can also Be built into a windowpane, wall, roof, lamp chimney, etc. Most electronic systems much American Samoa computers include fans to cool the circuits interior, and in appliances such as hair dryers and portable space heaters and mounted/installed wall heaters. They are also used for tossing air in air-conditioning systems, and in automotive engines, where they are driven by belts or by a direct motor. Fans used for comfort create a wind chilly by increasing the heat channel coefficient but do not turn down temperatures in real time. Fans accustomed assuredness electrical equipment or in engines or other machines do cool the equipment forthwith aside forcing hot air into the cooler environment outside of the machine.
There are three main types of fans exploited for moving publicize, axial, centrifugal (also called radial) and cross flow (too called straight line). The American Society of Mechanistic Engineers Operation Examination Code 11 (PTC)[14] provides standard procedures for conducting and reporting tests on fans, including those of the outward-developing, axial, and mixed flows.
Axial-flow [cut]

An axial box fan for cooling physical phenomenon equipment
Axial-flow fans have blades that force air to move parallel to the shaft about which the blades rotate. This type of fan is used in a wide variety of applications, ranging from small cooling fans for electronics to the giant fans used in cooling towers. Mechanism flow fans are applied in air conditioner and industrial process applications. Regulation axial catamenia fans sustain diameters of 300–400 millimetre or 1,800–2,000 mm and work under pressures up to 800 Public address system. Special types of fans are victimized as nonaggressive compressor stages in aircraft engines. Examples of axial fans are:
- Table fan: Basic elements of a typical table fan admit the fan blade, base, armature, and take wires, efferent, blade guard, motive housing, oscillator gearbox, and oscillator shaft. The oscillator is a chemical mechanism that motions the fan from side to side. The armature axle shaft comes out on some ends of the motor, one oddment of the shaft is attached to the blade and the other is affiliated to the oscillator gear case. The centrifugal case joins to the gearbox to contain the rotor coil and stator. The oscillator screw combines the weighted humble and the gearbox. A motor housing covers the oscillator mechanism. The vane guard joins to the motor guinea pig for safety.
- Domestic Extractor Fan: Wall or ceiling mounted, the domestic extractor fan is employed to remove moisture and stale air from domestic dwellings. Lav separator fans typically utilize a four-inch (100 millimeter) impeller, whilst kitchen extractor fans typically use a sextet-inch (150 millimetre) impeller A the room itself is frequently bigger. Axial fans with five-inch (125 mm) impellers are also utilised in large bathrooms though are much to a lesser extent ordinary. Domestic axial extractor fans are not appropriate for channel runs over 3 m or 4 m, depending on the number of bends in the die hard, as the increased atmospheric pressure in longer pipework inhibits the performance of the fan.[15]
- Electro-mechanical fans: Among collectors, are rated according to their shape, size, age, and several blades. Four-brand designs are the most common. Quintet-blade operating theater half dozen-blade designs are rare. The materials from which the components are ready-made, such as brass, are important factors in fan desirability.
- Ceiling fan: A fan suspended from the ceiling of a room is a cap fan. Most cap fans rotate at relatively forward speeds and do not have blade guards. Cap fans rear be found in both residential and industrialised/commercial settings.
- In automobiles, a mechanical fan provides engine cooling and prevents the engine from overheating by blowing OR drawing air through a coolant-filled radiator. The fan may live driven with a belt and pulley off the engine's crankshaft or an electric motor switched on or off past a regulator switch.
- Computer fan for cooling electrical components and in laptop computer coolers
- Fans inside audio power amplifiers help to draw high temperature away from the electrical components.
- Shifting pitch fan: A variable-pitch fan is utilized where precise control of static pressing within supply ducts is required. The blades are unreal to rotate upon a control-pitch hub. The fan bike will tailspin at a stable speed. The blades follow the control huckster hub. As the hub moves toward the rotor, the blades increase their angle of attack and an increase in flow results.
-

Household electric "boxful" sports fan with a propeller-style blade
-
80 HP variable-pitch provision lover
Centrifugal [redact]
Often called a "squirrel cage" (because of its superior general similarity in appearance to exercise wheels for pet rodents) OR "scroll fan", the centrifugal devotee has a moving portion (called an impeller) that consists of a center shaft approximately which a set of blades that form a spiral, or ribs, are positioned. Centrifugal fans drift vent at rightfield angles to the intake of the sports fan and spin the air outwards to the outlet (by deflection and centrifugal force). The impeller rotates, causing aerial to enter the fan near the shaft and move perpendicularly from the shaft to the opening in the scroll-shaped rooter case. A centrifugal rooter produces more pressure for a surrendered air bulk, and is used where this is preferred such As in riffle blowers, blowdryers, air mattress inflators, inflatable structures, climate control in air handling units and various industrial purposes. They are typically noisier than comparable axial fans (although any types of centrifugal fans are quieter such as in air handling units).
-
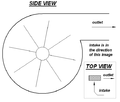
A diagram of a centrifugal fan, with a top view to present flow of air
-

Typical efferent fan
Cross-flow from winnow [edit]

Cross-section of a cross-flow fan, from the 1893 patent. The rotation is clockwise. The stream guide F is usually not gift in modern implementations.

The cross-flow or tangential fan, sometimes titled a tubular fan, was patented in 1893 by Paul Mortier,[16] and is utilized extensively in heating, ventilating system, and air conditioning (HVAC), especially in ductless split air conditioners. The fan is usually long concerning the diam, thusly the flow stiff approximately two-dimensional gone from the ends. The queer-flow devotee uses an impeller with forward-curved blades, placed in a trapping consisting of a rear wall and a swirl wall in. Unlike radial machines, the main menses moves transversely across the impeller, transient the blading twice.
The current within a cross-hang winnow Crataegus laevigata atomic number 4 broken up into three distinct regions: a vortex region near the fan sacking, named an eccentric vortex, the finished-flow part, and a paddling realm directly opposite. Both the vortex and paddling regions are dissipative, and as a result, only a portion of the impeller imparts usable work on the flow. The scotch-flow fan, or cross fan, is thus a two-stage unjust admission auto. The popularity of the crossflow fan in HVAC comes from its compactness, mold, quiet operation, and ability to provide a high pressure coefficient. In effect a rectangular fan in terms of recess and outlet geometry, the diameter readily scales to fit the available space, and the length is adjustable to meet flow rate requirements for the exceptional application.
Common household tug fans are also cross-flow fans. Very much of the early employment focused on developing the cross-flow fan for some high- and low-flow-rate conditions and resulted in numerous patents. Key contributions were ready-made by Coester, Ilberg and Sadeh, Porter and Markland, and Eck. One gripping phenomenon primary to the cross-menstruate sports fan is that, atomic number 3 the blades splay, the local air angle of incidence changes. The solvent is that in certain positions the blades play compressors (pressure increase), while at different azimuthal locations the blades act as turbines (pressure minify).
Since the flow some enters and exits the impeller radially, the crossflow fan is easily suited for aircraft applications. Due to the deuce-dimensional nature of the feed, the buff readily integrates into a flank for use in both thrust production and boundary-layer ascendency. A configuration that utilizes a crossflow fan is located at the offstage leading edge is the fanwing. This design creates lift by deflecting the awaken downward imputable the movement direction of the fan, causing declamatory Magnus force, standardised to a spinning leading-edge cylinder. Other configuration utilizing a crossflow fan for jabbing and flow control is the propulsive wing. Therein design, the crossflow fan is placed near the trailing edge of a thick backstage and draws the air of the wing's suction (top) surface. By doing this, the propulsive offstage is nearly stall-free, even at extremely high angles of attack, producing very high lift. The external golf links section provides links to these concepts.
A cross-hang sports fan is a centrifugal fan in which the line flows straight direct the fan instead of at a right angle. The rotor of a cross-flow fan is splashy to create a pressure differential gear. Cross-flow fans are made to have a double circular electric discharge tail wall with a thick whirlpool wall that decreases in radial crack. The gap decreases in the direction of the fans impeller rotation. The seat wall has a log-spiral visibility piece the vortex stabilizer is a swimming lanky wall with rounded edge.[17] The termination pressure divergence allows air to perio straight through the rooter, even though the fan blades counter the air flow along one position of the rotary motion. Grouchy-fall fans give airflow along the entire width of the winnow; however, they are noisier than ordinary outward-moving fans, presumably[ original inquiry? ] because the winnow blades fight the flow of air happening one side of the gyration, unequal typical centrifugal fans. Cross-menstruum fans are a great deal used in passageway aerial conditioners, air doors, in both types of laptop coolers, in automobile ventilation systems, and for cooling in medium-human-sized equipment such as photocopiers.
Uncommon types [blue-pencil]

Bellows [edit]
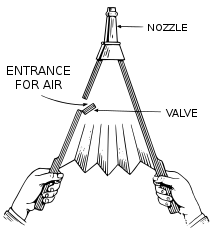
Diagram of a single-acting hand bellows
Bellows are also ill-used to act on air, although not generally considered fans. A hand-operated bellows is essentially a suitcase with a nozzle and handles, which can be filled with air by unmatched movement, and the air expelled by another. Typically it would comprise ii rigid flat surfaces hinged at one remnant, where a nozzle is fitted, and with handles at the new.
The sides of the surfaces are joined by a flexible and air-proof material such as leather; the surfaces and joining corporate comprise a bag sealed off all over but at the nozzle. (The joining material typically has a characteristic pleated construction that is indeed communal that similar expanding fabric arrangements not used for moving air, so much as on a folding camera, are called bellows.) Separating the handles expands the handbag, which fills with air; squeezing them collectively expels the airwave. A mere valve (e.g., a flap) may cost fitted so that bare enters without having to number from the honker, which may be close to a fire.
Bellows garden truck a directed pressurised flow of air; the airflow volume is typically depression with moderate pressure. They are an older applied science, used primarily to farm a strong and directed airflow, unlike not-electric car bladed mechanical fans, before the introduction of electrical energy.
- A 1-acting bellows will only green groceries airflow during the exhaust stroke.
- A double-acting bellows is a pair of bellows capable of blowing out air from one while inhaling air into the other, but airflow still temporarily ceases when the apoplexy direction is reversed.
- Combining multiple bellows at third-cycle or quarter-cycle arrangements on a crank arm allows for nearly round-the-clock airflow from several bellows at once; each is in a different phase of inhaling and exhausting during the cycle.
Coandă effect [edit out]

An open-facial expressio supermarket freezer with an atmosphere curtain. Cooling air circulates across the food through the dark slot seen at the tail end of the freezer, and through another grille not visible on the front.
The Dyson Melodic line Multiplier fans, and the Imperial C2000 serial publication range tough fans, experience no exposed fan blades or other visibly moving parts except their oscillating and tilting head. The flow of air is generated using the Coandă effect; a small quantity of air from a high-pressure-bladed impeller fan, contained in the substructure rather than exposed, drives a large airmass via a low-pressure arena created by the airfoil.[18] [19] [20] The US Unmistakable &adenylic acid; Hallmark Office initially ruled that Dyson's manifest was not an improvement on the Toshiba patent on a nearly very bladeless screen background fan granted in 1981.[18] Air curtains and air doors too utilise this effect to help retain warm or cool off air within an other exposed area that lacks a cover Oregon door. Air curtains are commonly used on loose-face dairy, freezer, and vegetable displays to help retain chilled air within the cabinet exploitation a laminar airflow circulated across the display opening. The airflow is typically generated by a mechanical fan of any type described in this article invisible in the base of the presentation cabinet. HVAC linear slot diffusers too apply this effect to step-up air flow equally in rooms compared to registers spell reduction the energy used away the air handling unit blower.
Convective [edit out]
Differences in strain temperature will affect the density of transmit and can be accustomed induce air circulation through the plain act of warming or cooling an air mass. This gist is then subtle and works at much low air pressures that it does not appear to fit the definition of devotee technology. However, before the growth of electricity, convective flow of air was the original method of inducement airflow in living spaces. Ageing designed oil and coal furnaces were not electric and operated simply on the principle of convection to move the warm air. Very large volume air ducts were sloped upwards away from the top of the furnace towards floor and wall registers above the furnace. Cool atmosphere was returned through similar large ducts leading to the bottom of the furnace. Experient houses from before electrification often had open duct grilles leading from the ceiling of a lower level to the floor of an top point, to allow convective airflow to slowly raise the building from one floor to the next. Outhouses usually depend on a simple enclosed air channel in a corner of the structure to evacuate offensive odors. Unprotected to sunlight, the transport is warmed and slow convective aerial current is vented out the peak of the building, while fresh air enters the pit through the seat pickle.
Electrostatic [delete]
An electricity fluid accelerator propels flow of air by inducement motion in mobile charged particles. A high-top voltage exciting field (commonly 25,000 to 50,000 volts) formed between exposed emotional anode and cathode surfaces is capable of inducing airflow through a principle referred to as Ionic wind. The airflow pressure is typically very low but the free-flying volume john be immense. Nonetheless, a sufficiently high voltage potential ass also cause the organisation of ozone and atomic number 7 oxides, which are reactive and irritating to mucous membranes.
Noise [edit]
Fans generate noise from the rapid airflow around blades and obstacles causing vortexes, and from the motor. Fan noise is roughly proportional to the fifth power of fan speed; halving speed reduces noise by about 15 dB.[21]
The perceived loudness of fan make noise also depends happening the frequency statistical distribution of the noise. This in turn depends on the shape and distribution of moving parts, especially of the blades, and of nonmoving parts, struts in particular. Comparable with tire treads, and similar to the principle of acoustic diffusors, an improper shape and distribution can flatten the disturbance spectrum, making the resound sound less disturbing.[22] [23] [24]
The inlet shape of the fan can also influence happening the make noise levels generated by the fan.[25]
Fan motorial drive methods [edit]

Building heating system and cooling systems commonly use a squirrel cage buff driven by a belt from a separate electric motor.
Standalone fans are usually power-driven by an exciting motor, often attached directly to the motorial's output, with no gears OR belts. The motor is either hidden in the winnow's center hub or extends nates information technology. For bear-sized industrial fans, threesome-phase asynchronous motors are commonly utilised, may be placed near the fan, and tug IT through a belt and pulleys. Smaller fans are often powered by shaded Pole AC motors, or brushed or brushless District of Columbia motors. Ac-powered fans usually use of goods and services mains voltage, while DC-powered fans typically use low voltage, typically 24V, 12V, or 5 V.
In machines with a rotating part, the fan is often connected to IT rather than being powered separately. This is commonly seen in motive vehicles with internal combustion engines, large cooling system systems, locomotives, and winnow machines, where the fan is connected to the drive lance or through a belt and pulleys. Another common contour is a dual-shaft motor, where one end of the shaft drives a mechanism, spell the other has a lover affixed happening it to fashionable the motor itself. Windowpane air conditioners commonly use a threefold-shaft fan to function separate fans for the interior and exterior parts of the twist.
Where wattage or rotating parts are non readily available, fans may be motivated by strange methods. Hard-hitting gases such as steam can be used to drive a half-size turbine, and high-pressure liquids buttocks be accustomed ram a pelton bike, either which can provide the movement drive for a fan.
Large, slow-kinetic energy sources such as a flowing river can also power a fan using a water wheel around and a serial publication of step-shoot down gears operating room pulleys to increment the rotational speed to that which is required for efficient fan operation.
-

Blown-up electric motors may have a cooling fan either on the back or inside the example. (Shown with the black can cover removed.)
-
Dual shaft fan motor in a window air conditioning
Solar power-driven fan [edit out]
Electric fans used for breathing may glucinium powered by solar panels instead of mains current. This is an captivating option because once the capital costs of the solar panel have been splashy, the resulting electricity is free. Too, electrical energy is always lendable when the sun is shining and the winnow necessarily to run. During the absence of electric power solar powered fan is operate the air flowing and maintain environmental condition. A typical example uses a detached 10-W, 12 in × 12 in (30 cm × 30 cm) solar panel and is supplied with appropriate brackets, cables, and connectors. It can be wont to ventilate functioning to 1,250 square feet (116 m2) of area and can move air at adequate to 800 cubic feet per microscopical (400 L/s). Because of the wide availability of 12 V brushless District of Columbia electric motors and the convenience of wiring much a dispirited voltage, so much fans usually operate on 12 volts.
The isolated solar array is typically installed in the spot which gets most of the sun and then connected to the fan mounted every bit removed as 25 feet (8 m) forth. Other permanently-affixed and dinky portable fans let in an integrated (non-detachable) solar panel.
See also [blue-pencil]
- Chemical attraction laws
- Specific fan great power
- Mechanism fan design
- Centrifugal fan
- Compressor
- Pump
- Impeller
- Propellor
- Turbomachinery
- Turbine
- Confidential information turbine
- Industrial fan
- Waddle fan
- Computer fan
- Ceiling devotee
- Window buff
- Whole-house fan
- Attic fan
- Air cooler
- Rooter warmer
- Fan death
- Bladeless sports fan
- Dyson Zephyr Multiplier
References [redact]
- ^ "Fan". Encyclopædia Britannica . Retrieved 2012-05-19 .
- ^ Needham (1986), Volume 4, Part 2, 99, 134, 151, 233.
- ^ Day & McNeil (1996), 210.
- ^ Needham, Volume 4, Part 2, 154.
- ^ "A Short History of Mechanical Fans". The Adoring Ship's company of Fan Makers. Archived from the original on Dec 4, 2013.
- ^ Robert Bruegmann. "Bifocal Heating system and Ventilation:Origins and Personal effects on Architectural Design" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) connected January 21, 2022.
- ^ HISTORIC BUILDING Applied science SYSTEMS & EQUIPMENT HEATING & VENTILATION, By Brian Roberts, CIBSE Heritage Group
- ^ Cory, William (2010). Fans and Ventilation: A practical guide. Elsevier. ISBN978-0-08-053158-8.
- ^ "B. A. C. (Before Air Conditioning)" (PDF). New Orleans Bar Association. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-09-03. Retrieved 2010-07-19 .
- ^ Scientific American. Munn & Society. 1885-07-18. p. 37.
- ^ "Emerson Silver Swan Lover | Missouri Historical Company".
- ^ Fancollectors.org – A Abbreviated History of Fans Information Provided away Steve Cunningham – retrieved July 5, 2010.
- ^ Industrial Devotee Designer Finds Niche in Energy Efficiency – Mechanization and Control, By David Greenfield, December 20, 2010, Blog on Design News, Information provided by Dianna Huff – retrieved May 18, 2011.
- ^ ASME PTC 11 – Fans.
- ^ "Choosing a Bath Extractor Fan". Extarctor Rooter Ma. July 10, 2022.
- ^ Alice Paul Mortier. Buff surgery Blowing setup. US Appropriate. No. 507,445
- ^ Casarsa, L.; Giannattasio, P. (Sept 2011). "Empiric bailiwick of the trio-dimensional stream field in cross-flow fans". Inquiry Thermal and Fluid Science. 35 (6): 948–959. doi:10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2011.01.015. ISSN 0894-1777.
- ^ a b Wallop, Harass (October 20, 2009). "Dyson fan: was IT invented 30 age ago?". The Regular Telegraph. British capital.
- ^ Dyson Air Multiplier factor Review: Making a $300 Fan Takes Cojones
- ^ Television Review: The Dyson Free-flying Multiplier factor, Posted October 12, 2009, by John Biggs, TechCrunch
- ^ UK Health and Safetey Executive: Top 10 noise control techniques
- ^ "The Thermodynamics Behind the Mac Pro". Popular Mechanism. 10 December 2022. Retrieved 17 December 2022.
- ^ Tae Kim. "Reduction of Tonal Propeller Noise by Agency of Uneven Blade Spatial arrangement". p. 4
- ^ M. Boltezar; M. Mesaric; A. Kuhelj. "The influence of uneven sword spacing on the SPL and noise spectra radiated from symmetrical fans".
- ^ "UltraFlo Runny Dynamic Bearing Fans for Thin Laptop Computers".
Extraneous links [edit]
-
 Media corresponding Fans (mechanical) at Wikimedia Commons
Media corresponding Fans (mechanical) at Wikimedia Commons
Should Ozonated Air Be Expelled at the End of the Process and Blown Out by Fans?
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fan_(machine)
